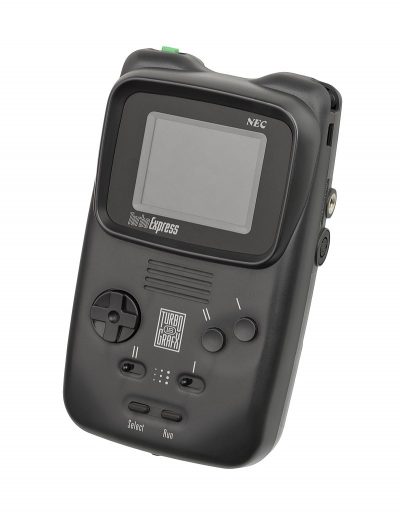
The TurboExpress is an 8-bit handheld game console by NEC Home Electronics, released in late 1990 in Japan and the United States, branded as the PC Engine GT in Japan and TurboExpress Handheld Entertainment System in the U.S. It is essentially a portable version of the TurboGrafx-16 home console that came two to three years earlier. Its launch price in Japan was ¥44,800 and $249.99 in the U.S.The TurboExpress was technically advanced for the time, able to play all the TurboGrafx‑16’s HuCard games, featuring a TV tuner and a backlit, active-matrix color LCD screen.The TurboExpress primarily competed with Nintendo’s Game Boy, Sega’s Game Gear, and the Atari Lynx. With 1.5 million units sold, far behind its two main competitors, NEC failed to gain significant sales or market share in the handheld market.